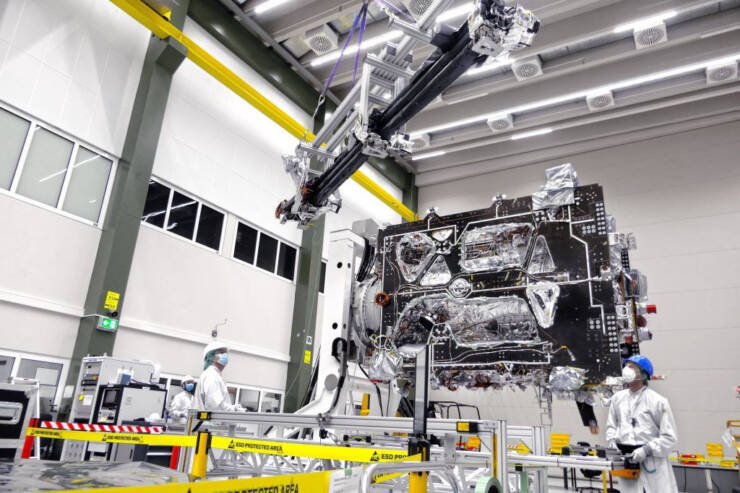
Friedrichshafen, Germany. JUICE, the European Space Agency’s JUpiter ICy moons Explorer mission, has successfully passed its latest milestone: space engineers at Airbus’ satellite integration centre in Friedrichshafen (Germany) have attached the magnetometer boom (MAGBOOM) to the spacecraft. The MAGBOOM carries five magnetically sensitive instrument sensors to keep them far from any disturbances from the main spacecraft. The sensors are part of the magnetometer J-MAG and the Radio and Plasma Wave Investigation (RPWI) scientific instruments.
J-MAG is a magnetometer package to study the Jovian magnetosphere and its interaction with the three icy moons, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto, in particular with Ganymede´s intrinsic magnetic field. The RPWI instrument will investigate the radio emissions and plasma environments of Jupiter and its icy moons.
The MAGBOOM is made of non-magnetic materials, such as carbon fiber, various titanium and aluminum alloys, and bronze and weighs 44 kilograms (including the sensors). The boom must withstand temperatures from -210° to +250° Celsius. Once deployed its total length is 10.6 metres.
The 6.2 ton JUICE spacecraft will set off in 2022 on its near 600 million-kilometers-long journey to Jupiter. The spacecraft will carry 10 state-of-the-art scientific instruments, including camera, spectrometers, a sub-mm wave instrument, an ice-penetrating radar, a laser altimeter, a radio-science experiment and instrument packages to monitor the magnetic and electric fields and charged particles.
JUICE will spend more than three years around the gas giant, completing a unique tour that will include in-depth studies of three potentially ocean-bearing moons, Ganymede, Europa and Callisto and collecting data to provide answers on the conditions for emergence of life around a giant planet. It will perform a multidisciplinary investigation of the Jupiter system as an archetype for gaseous planets. It will spend nine months orbiting the icy moon Ganymede analysing its environment, surface, interior and its potential habitability.
As prime contractor, Airbus is leading an industrial consortium of more than 80 companies across Europe.








