Warren Buffett, the renowned investor, made a thought-provoking observation during the 2008 financial crisis. He noted that the term “weapons of mass destruction” isn’t limited solely to nuclear weapons; it extends to encompass various other realms, including financial instruments.
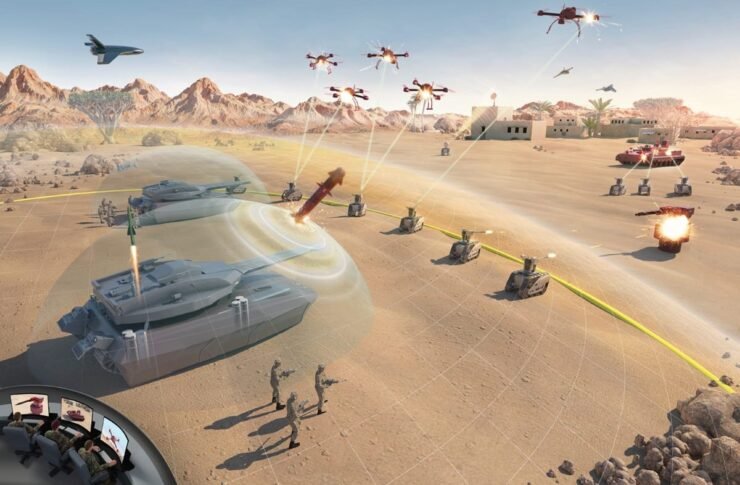
In the ever-evolving landscape of warfare, technological advancements have ushered in a new era of strategic possibilities. The integration of long-range missiles, precision-guided smart weapons, unmanned systems, robots, and satellites has given military strategists a transformative edge. This paradigm shift in warfare, driven predominantly by cutting-edge technology, is aptly coined as “Non-Contact” or “Non-Contact Warfare.”
In essence, this form of warfare leverages a comprehensive utilisation of national capabilities in a seamlessly integrated fashion. Its primary objective is to achieve swift and decisive victories by remotely disrupting, denying, and destroying the enemy’s war-waging potential. This is executed through the precise delivery of destructive kinetic energy and the strategic application of soft power, facilitated by relentless information operations.
The overarching goal is to dismantle the enemy’s command and control systems and war infrastructure. This comprehensive approach encompasses information warfare and operations, missile warfare, remote warfare through drone attacks, and the strategic integration of robotics. All of this unfolds within an environment characterised by battlefield transparency and facilitated by cutting-edge Command, Control, Communication, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition, and Reconnaissance (C4ISTAR) systems.
Former Army chief General Bipin Rawat emphasised the imperative role of the Army in embracing technological advancements, stressing the significance of non-contact warfare as a pivotal strategy for gaining an edge over adversaries in the future.
Former Army chief General Bipin Rawat emphasised the imperative role of the Army in embracing technological advancements, stressing the significance of non-contact warfare as a pivotal strategy for gaining an edge over adversaries in the future
General Rawat, in remarks made a few years ago, highlighted the growing relevance of non-contact warfare in the landscape of upcoming conflicts. He clarified that this shift towards non-contact warfare doesn’t diminish the importance of the infantry—the soldiers on the ground armed with rifles—whose relevance will persist across ages.
The General underscored that non-contact warfare is poised to provide a crucial advantage in future conflicts. He emphasised the necessity of comprehending the specific context that demands a strategic move in this direction. In essence, General Bipin Rawat’s perspective echoed the conviction that leveraging technological innovations and embracing non-contact warfare is essential for maintaining a strategic advantage in the evolving dynamics of modern warfare.
Implications and world at large
When it comes to modern warfare, cyber warfare has become an indispensable component, seamlessly integrated into military strategies. The United States Department of Defence defines cyber operations as the integrated employment of Electronic Warfare (EW), Computer Net Operations, Military Deception, Psychological Operations, and Operational Security. This orchestrated approach aims to influence, disrupt, correct, or undermine the adversary’s decision-making processes while safeguarding one’s own interests.
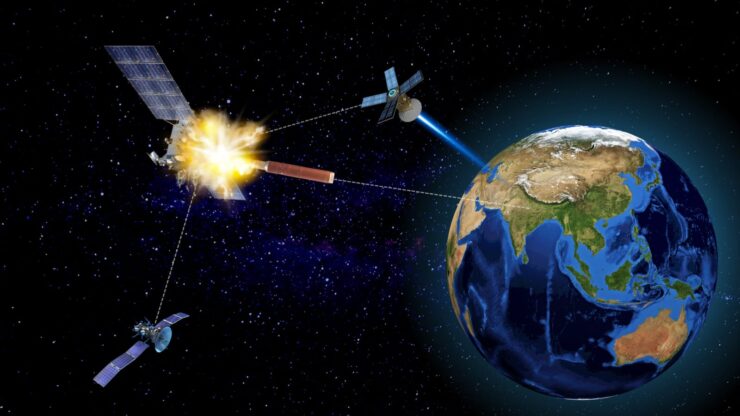
In the realm of artillery, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) take centre stage, directing fire assaults and conducting Post Strike Damage Assessment (PSDA) for any firepower engagement. The utilisation of satellites, UAVs, and on-the-ground agents in enemy territory plays a pivotal role in target acquisition for Missiles and Precision Guided Munitions (PGMs), aligning with the broader strategy of Non-Contact Warfare.
Artificial intelligence, notably in the form of robotics, emerges as a significant player in this paradigm. Robots equipped for multifaceted soldiering tasks, coupled with Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) and Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs), revolutionise operations in both land and sea theatres.
Artificial intelligence, notably in the form of robotics, emerges as a significant player in this paradigm. Robots equipped for multifaceted soldiering tasks, coupled with Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) and Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs), revolutionise operations in both land and sea theatres
Delving into the specifics of Non-Contact Warfare, envisioning its application in an advanced armed forces scenario unfolds a strategic sequence. The initiation involves targeting communication and reconnaissance satellites in outer space. Subsequent stages encompass Information Operations, designed to disorient and confuse the enemy by manipulating power grids and disseminating false information. The culmination of this orchestrated assault involves a barrage of artillery and missiles. Finally, the deployment of robots via unmanned helicopters takes the forefront in ground combat, seizing objectives and paving the way for the subsequent entry of ground troops to secure the area through strategic link-ups.

Wars of the 21st Century and India’s Need of the hour
During a recent workshop organised by CUTS International on ‘Deliverables to Deliveries’, Stories of U.S.-India Defense and Security Partnership, Lt Gen Subrata Saha (retd), Former Deputy Chief of Army Staff posed a critical question during his address at an event, prompting a profound examination of the evolving nature of threats. He asked, “Given the kind of threats that are evolving, do we have the luxury anymore to be as deliberate as we have been in the past?”
This thought-provoking question serves as a catalyst for discussions on the concept of future warfare. Lt Gen Saha goes on to assert that the nation is already embroiled in a state of grey zone war with China, constituting a significant threat. He draws attention to the intricate web of geopolitical complexities, including a nexus between China and Pakistan, the establishment of submarine bases in Bangladesh and Myanmar, and a new government in the Maldives that has expressed the desire for the withdrawal of Indian military forces in its initial interactions with an Indian minister. Lt Gen Saha suggests that behind these developments, discernible forces are at play.
Considering this geopolitical landscape, Lt Gen Saha contends that the nation is standing on the precipice of non-contact warfare, a future paradigm where traditional military strategies may no longer be as effective.
Lt Gen Subrata Saha’s insights underscore the imperative for India to prepare for potential threats in various domains. In the realm of space, he emphasises the need for India to anticipate and mitigate threats to its space assets
What India should be prepared for?
Lt Gen Subrata Saha’s insights underscore the imperative for India to prepare for potential threats in various domains. In the realm of space, he emphasises the need for India to anticipate and mitigate threats to its space assets. The effects of such threats could be far-reaching, impacting communications, command and control systems, intelligence gathering, surveillance capabilities, and the utilisation of sensors and weapon systems.
In the context of cyber threats, it is essential to point to the experiences of the previous year, highlighting the clear and present danger posed by cyber adversaries. The nature of these threats, whether in the public domain or undisclosed, represents a significant challenge that requires comprehensive cybersecurity measures.
Additionally, the reference to the cutting of subsea cables off the coast of Taiwan serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities associated with undersea communication infrastructure. Given India’s extensive network of subsea cables that connect it with the rest of the world, addressing potential threats to this vital connectivity becomes a critical consideration. The collaborative nature of addressing such challenges, emphasising that no single country, including India or the United States, can effectively deal with these threats alone. The necessity for like-minded nations to join forces in confronting emerging threats in this century becomes paramount for collective security and resilience.

Incoming Autonomous Threats
The importance of acknowledging and addressing the autonomous systems being developed, particularly by the People’s Republic of China stands unavoidable. The advancement and public display of such autonomous technologies present a strategic consideration for India, highlighting the need to stay abreast of technological developments that could impact national security.
Looking beyond traditional warfare, the multifaceted nature of future conflicts should be sketched out with gravity. Information warfare, psychological warfare, propaganda, influence operations, and electoral manipulation are identified as key elements in the arsenal of contemporary warfare. And pointing to instances, such as the alleged manipulation of Canadian elections by China, as indicative of the evolving strategies employed by state actors to achieve their objectives.
Recognizing the interconnected and global nature of these challenges, the inadequacy of individual countries dealing with such threats alone gets naturally highlighted. A collaborative approach, stressing the importance of like-minded nations coming together to address the complexities of modern warfare should not go unseen. This collective effort becomes essential to confront the diverse array of challenges that exploit social, cultural, and political fault lines, requiring a united response to safeguard shared interests.
Looking beyond traditional warfare, the multifaceted nature of future conflicts should be sketched out with gravity. Information warfare, psychological warfare, propaganda, influence operations, and electoral manipulation are identified as key elements in the arsenal of contemporary warfare
The Bottom Line
The emerging era indeed emphasises the strategic significance of technology and its role in shaping the battlefield. In light of this transformative shift, the call for much deeper, stronger, and comprehensive partnerships with like-minded nations becomes imperative. Collaborative efforts enable the pooling of resources, sharing of technological expertise, and the development of joint strategies to effectively navigate the challenges presented by the evolving nature of warfare.
These partnerships extend beyond traditional military alliances and encompass collaborative initiatives in areas such as intelligence sharing, cybersecurity, technological innovation, and diplomatic efforts. Recognizing shared values and interests, like-minded nations can forge alliances that enhance their collective capabilities, resilience, and ability to respond to multifaceted threats.
-The writer is a passionate independent journalist with a keen focus on Space and Defence Affairs and is associated with Raksha Anirveda as senior defence correspondent. He can be reached at vaibhavmag1@gmail.com & he tweets @VaibhavMAG















