Space plays a crucial role in military operations, as evidenced by its utilisation in the Gulf Wars, US engagement in Afghanistan, and the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. It provides a significant advantage to land-based operations and is considered the new high ground for military strategies. Recent conflicts have demonstrated that both commercial and military space capabilities can be effectively employed for beyond-line-of-sight communications, Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT), weather forecasting, terrain and environmental monitoring, as well as intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR). The integration of these space-enabled enhancements with military operations improves battlefield awareness and creates opportunities for innovative use at the tactical and operational levels, as seen in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
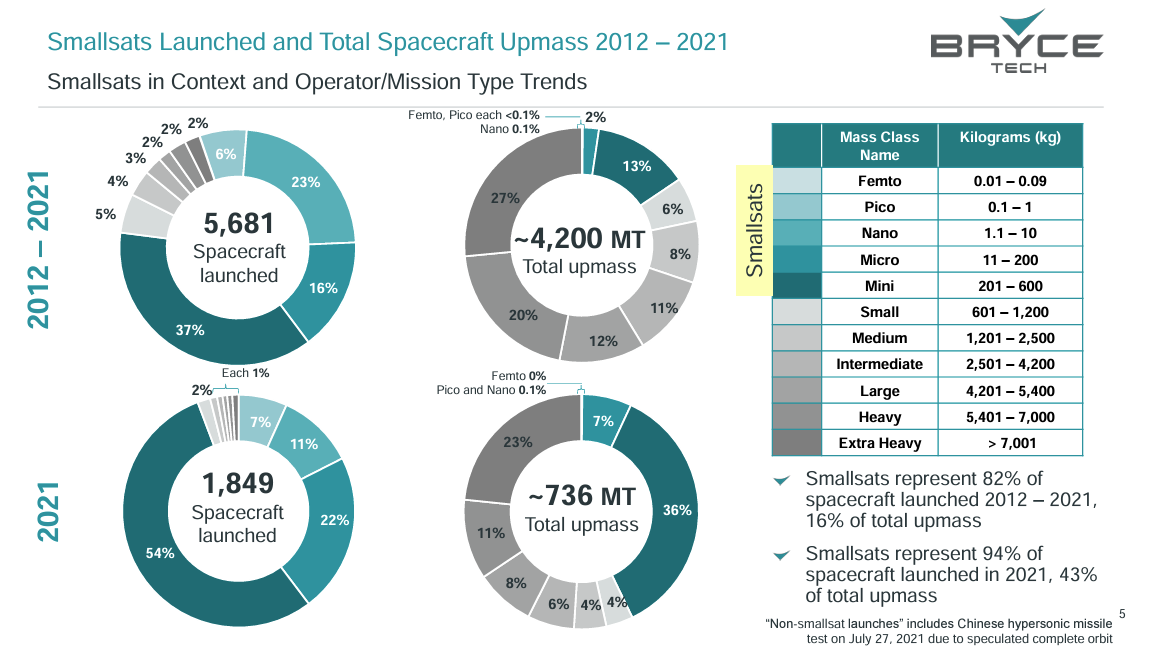
In the past, military satellites were expensive and heavy, limiting their availability to a select few nations. However, advancements in electronic, electrical, and optical technologies have made it possible to miniaturise components, resulting in the development of small satellites. This technological progress, coupled with innovation, has created an ecosystem of small satellites. The number of small satellites in orbit has increased rapidly over the last decade, and the industry is experiencing a significant amount of investment, leading to an increase in the launch, development, and operation of small satellites. The infographic illustrates the growth of small satellites in the last decade.
Small satellites, owing to the miniaturisation of key components and technological innovation, can now provide high-quality data and services across various space-based capabilities. While the technical capabilities of a small satellite may be less than those of a larger satellite of the same type, several attributes make their military use operationally advantageous.
Key attributes of small satellites
Lower Cost: The reduced development costs and technological innovations, coupled with large-scale manufacturing, further drive down the costs of smaller satellites. In comparison to traditional large satellites that cost hundreds of millions of dollars to develop, small satellites can be built for one-tenth or even less, making them commercially feasible and enabling new capabilities and applications.
The number of small satellites in orbit has increased rapidly over the last decade, and the industry is experiencing a significant amount of investment, leading to an increase in the launch, development, and operation of small satellites
Manufacturing at Scale: Small satellites are often deployed in large constellations with relatively short lifespans, requiring fast replacements. This necessity leads to production at mass scales using efficient assembly-line processes, further decreasing costs and development time.
Frequent Technological Upgrades: Due to the quicker replacement of satellites in orbit and shorter development cycles, small satellites facilitate frequent technological upgrades.
On-orbit Technology Testing: With a lifespan of 1-3 years and lower costs, small satellites enable the testing of technologies in orbit.
Short Development and Deployment Cycle: Small satellites have a relatively short development and deployment cycle, making it easier to improve the manufacturing process and train the space domain workforce.
Huge Constellations: Small satellites enable the creation of large constellations, offering advantages such as increased temporal resolution or revisit rate. This is possible due to short development and manufacturing times and lower costs.
Formation Flying: Given the cost advantage, it is feasible to develop multiple small satellites designed to work in tandem. This opens up numerous opportunities, such as having multiple satellites with different sensors flying over the same area simultaneously, allowing for tip and cue, data fusion, and other innovative uses.
Military Significance of Small Satellites
Small satellites have become increasingly crucial in military operations due to the benefits they offer. Primarily utilised in Low Earth Orbit, launching these satellites is cost-effective and more accessible. Simultaneously, the detailed images/data received and faster communication provide crucial advantages in military operations. The emerging ecosystem that facilitates deploying small satellites in large numbers has the potential to impact military operations at both tactical and operational levels.
The faster information and improved communication offered by small satellites for land forces can enhance the effectiveness of various offensive systems at tactical, operational, and strategic levels. Additionally, they strengthen defensive systems by providing early warnings.
The Ukrainian forces have demonstrated innovative use of Starlink satellite systems, showcasing the potential achievements using small satellites during conflicts. According to Chinese researchers, the recent US Defence Department contract with SpaceX has the potential to increase data transmission for drones and fighter aircraft by 100 times.
The potential for utilising small satellites in the military is immense. Militarily significant aspects of small satellites are enumerated below.
High Revisit Rate & Tactical Use of Space-Based Imagery: Small satellite constellations equipped with EO/IR/SAR offer an exceptionally high revisit rate, providing military decision-makers with close-to-real-time operational and intelligence inputs. The integration of the latest artificial intelligence capabilities in data processing shortens the decision-making process. This capability to generate massive amounts of data almost in real time creates an opportunity to use space-based imagery at the tactical level.
The faster information and improved communication offered by small satellites for land forces can enhance the effectiveness of various offensive systems at tactical, operational, and strategic levels. Additionally, they strengthen defensive systems by providing early warnings
Targeting: Networking satellites with drones and ground attack munitions/missiles significantly alters the military’s targeting paradigm. Project Convergence, the US Army’s testing of new space capabilities to improve targeting and networks, reported shortening the sensor-to-shooter timeline from 20 minutes to 20 seconds. Space-based communications also facilitate the creation of networked missiles, allowing mid-flight re-programmability to react to changes in battlefield target requirements.
Communications: Mega constellations using small satellites in low Earth orbit offer consistent global coverage with very low latency. Such communication/data services provide a force multiplier effect for special operations and out-of-area contingencies, as well as effective communication means in conflict zones.
Internet of Military Things (IoMT): IoMT is a network of interconnected sensors or “things” in the military domain. These sensors communicate, coordinate, and interact with the physical environment, increasing intelligence and allowing for more informed decision-making. IoMT presents an opportunity for enhancing capabilities in various areas of the military. Some use cases for the IoMT include:
Border Management: Indian security forces, having thousands of kilometres of border in difficult terrain to monitor against threats, can deploy satellite-connected sensors detecting movement or activity along the borders, alerting troops to possible intrusions and enabling a better and more effective response.
Garrison/Base Security: A small satellite-based network can also be used for large garrison/base security by employing appropriate sensors, making security more responsive and effective.
Managing Battle Casualties: Using sensors, critical medical parameters of an injured soldier in the combat zone can be monitored. The collected data can then be shared with doctors/specialists in real-time, enabling remote casualty management, which is essential for critical intervention.
Formation Flying: The concept of formation flying satellites involves multiple satellites with onboard control to maintain relative positions and preserve an appropriate topology. This entails several satellites arranged to function as a single, large, and virtual instrument. For instance, the “SAR Mirror” design envisions a large synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite surrounded by a swarm of small satellites equipped with receivers, each capable of detecting radar echoes and relaying them to the primary satellite. Similarly, a formation of Earth observation (EO) satellites could provide an image of the ground target from different angles simultaneously, enhancing swath width. The US Space Force recently announced the use of new satellite swarms equipped with infrared detectors in low Earth orbit (LEO) as part of their missile defence strategy to improve detection sensitivity and the timeliness of missile warnings.
India needs to swiftly enhance its small satellite capabilities to keep pace with military communication, ISR, and PNT capabilities and to counter China’s offensive capabilities in space warfare. Small satellites can significantly enhance the operations of the Indian Armed Forces at both operational and tactical levels
Operationally Responsive Space: Due to their very short development times and low costs, small satellites can be rapidly replaced in orbit. This allows for the addition of satellites with new technologies or increased revisit capabilities. During conflicts, a constellation that has been attacked by an adversary can be quickly reconstituted, enhancing resilience. Low costs also facilitate the stockpiling of satellite reserves, achieving a launch-on-demand capability. Resilience: Small satellite constellations offer a crucial advantage — resistance to kinetic attacks, such as anti-satellite weapons. While large satellites are considered easy targets, the destruction of one or more small satellites would not significantly impact space-based capabilities. This deters adversaries from launching this type of attack.
Commercial Capabilities: Much of the recent development in small satellite systems has occurred in the commercial sector. The primary benefit is the ability of military users to leverage existing commercial systems for military purposes, avoiding the need to develop new systems and resulting in significant cost savings. It is essential to note that commercial assets need to be considered national assets for assured availability during times of conflict.
Satellite Tracking, Safety of Flight, and Space Traffic Management: While the minimal size of small satellites provides several advantages, one major challenge is the difficulty of detecting and tracking them in orbit. This limitation can hinder Space Domain Awareness and increase the risk of collisions in orbit. The large number of small satellites, especially mega constellations comprising thousands of satellites, amplifies the challenges of ensuring orbital safety.

Small Satellites – What are the US and China Doing
US: Small satellites are increasingly vital for military use, with both the US and China heavily investing in their development. The US Space Force is shifting away from relying on large, expensive satellites in favour of smaller, more resilient constellations. The space acquisition tenets issued on Oct 22 have listed building smaller satellites as the first tenet, clearly indicating the importance of small satellites to the US Space Force. This shift is expected to improve missile warning capabilities and enhance military communication networks.
China: While detailed information on China’s programs for developing small satellites for military use is not available, recent developments highlight the country’s achievements and ongoing progress in the small satellite space. China is advancing its small satellite capacity and plans to launch a 13,000-satellite constellation to rival Western projects. Open sources indicate that the Chinese government has established two manufacturing plants capable of producing over 400 small satellites per year to support this ambitious effort.
Small Satellites for the Indian Armed Forces
India needs to swiftly enhance its small satellite capabilities to keep pace with military communication, ISR, and PNT capabilities and to counter China’s offensive capabilities in space warfare. Small satellites can significantly enhance the operations of the Indian Armed Forces at both operational and tactical levels. Over the past five years, various policies and initiatives have been implemented to develop the Military-Civil ecosystem in the country for satellite technology and manufacture. This, combined with the technical prowess of ISRO, has led to the establishment of a vibrant small satellite ecosystem in the country. However, certain recommendations for fast-tracking capability achievement include:
Space Roadmap: An industry version of the roadmap for enhancing the space and small satellite capabilities of the Armed Forces will help the industry prepare and expand to meet the demands of the Armed Forces.
Small satellites are poised to be a game-changer for military operations. However, two major technological challenges for small satellites are propulsion systems affecting manoeuvrability and communication means limited by power availability. Various efforts are underway to miniaturise and develop alternatives to address these challenges
Procurement Policies: Special acquisition procedures tailored to the nuances of the satellite manufacturing ecosystem are needed to facilitate the procurement of satellites and related capabilities. Simplified procurement procedures, startup-friendly funding mechanisms, and export promotion are recommended policy changes.
Technology Development Initiatives: While initiatives like IDEX and TDF provide a valuable platform for firms to participate in developing niche technologies for the space sector, there is a need to refine procedures, improve funding amounts, and establish linkages to guaranteed orders.
Market Creation: The government should lead in placing orders to create a market for space-related products. Risk-sharing vehicles for technological development and innovation should also be established.
Key Takeaways
Small satellites are poised to be a game-changer for military operations. However, two major technological challenges for small satellites are propulsion systems affecting manoeuvrability and communication means limited by power availability. Various efforts are underway to miniaturise and develop alternatives to address these challenges.
Planning and implementation are crucial at this juncture to leverage the opportunities provided by this technological shift. The small satellite revolution, primarily led by the commercial sector, is already underway. Military forces stand to benefit by utilising commercial offerings and exploring military-specific opportunities. Small satellites offer cost savings, the latest technologies, near-constant surveillance, increased transparency, and tactically relevant satellite imagery. However, careful consideration is required to address challenges related to space tracking and space traffic management. By leveraging small satellites thoughtfully and proactively, militaries can gain significant strategic advantages.
-The writer has diverse military experiences, including service in organisations related to space and defence procurement. Presently, he holds the position of VP Growth Operations at Dhruva Space. The views expressed are personal and do not necessarily reflect the views of Raksha Anirveda
The writer is a veteran with more than three decades of military service and a former UN peacekeeper. He has served in various military organisations related to Operations, and Space & Defence procurement. He is currently Vice President - Growth Operations at Dhruva Space. The views expressed are of the writer and do not necessarily reflect that of Raksha Anirveda






