TOULOUSE: The SCARBO (Space CARBon Observatory) project for improved measurement of greenhouse gases has been officially kicked off. It is funded by the European Union (EU) Horizon 2020 Programme and will be implemented by a consortium of seven European organisations led by Airbus on May 25.
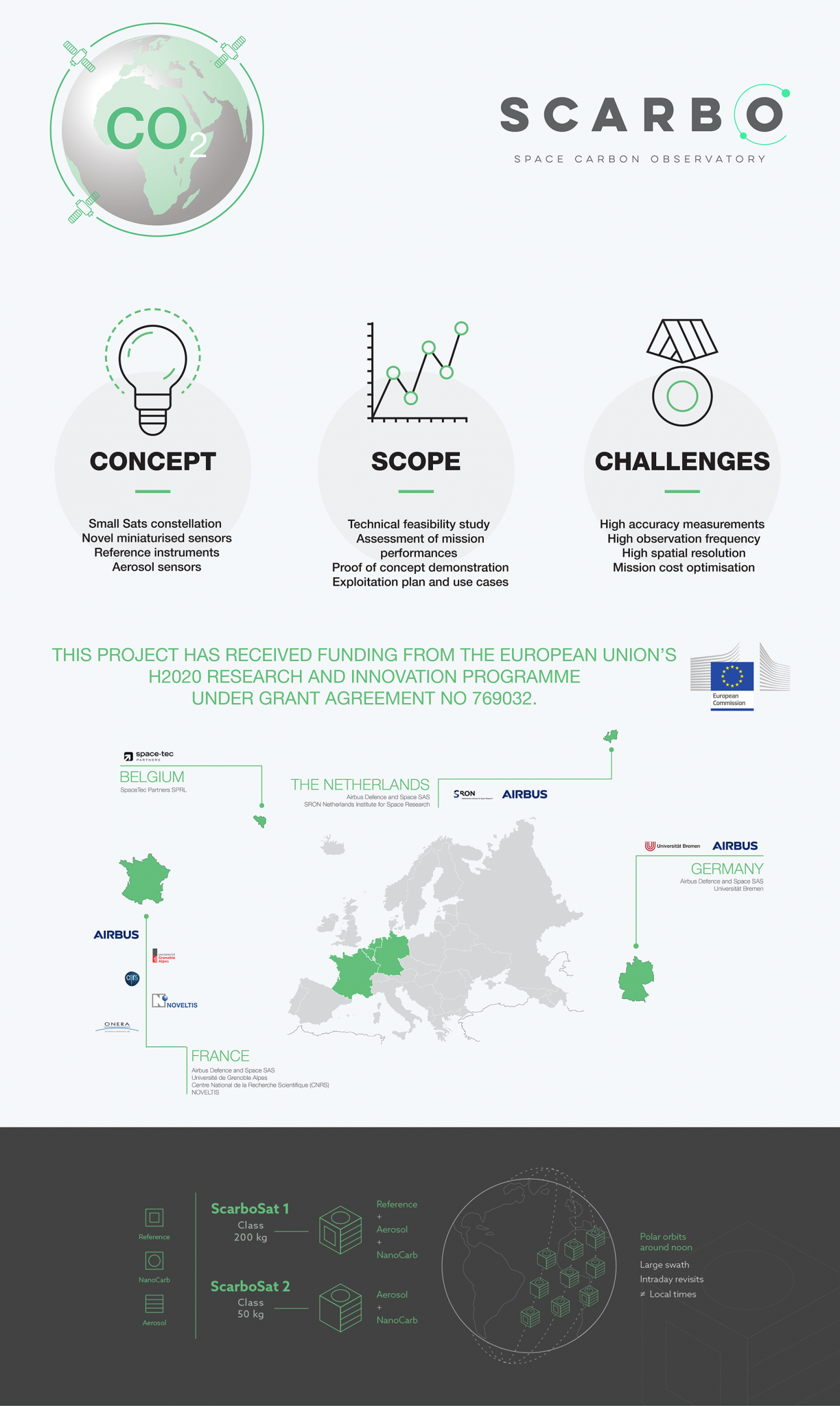
The project aims at solving a key challenge of anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) monitoring from Space: improvement of the temporal revisit over the various sites of interest while increasing the accuracy and resolution of measurements. This is envisaged by implementing a novel miniaturised static spectrometer concept on a constellation of small satellites coupled with aerosol sensors and high end reference instruments.
A few days ago the consortium held its first User Advisory Board at Airbus in Toulouse, France, to ensure all key users’ needs (international, national and local institutions, European Commission, downstream industry and Space Agencies) are considered in the solution definition.
 “The emerging policy needs for anthropogenic greenhouse gases monitoring from Space call for frequent observations, high accuracy and spatial resolution. To this end the Commission is currently considering to possibly expand its constellation of Copernicus satellites. With SCARBO, we could go beyond what Copernicus can do and complement the tremendous data provided by the Sentinels,” said Hugo Zunker, Copernicus Policy officer at the European Commission.
“The emerging policy needs for anthropogenic greenhouse gases monitoring from Space call for frequent observations, high accuracy and spatial resolution. To this end the Commission is currently considering to possibly expand its constellation of Copernicus satellites. With SCARBO, we could go beyond what Copernicus can do and complement the tremendous data provided by the Sentinels,” said Hugo Zunker, Copernicus Policy officer at the European Commission.
“Airbus is thrilled to lead this initiative, which is part of our continuous drive to bring disruptive technology to the space business by seeking new flexible and affordable solutions. We are strongly committed to the world’s effort to combat climate change and its impacts to our planet: with SCARBO we are proud to contribute to the United Nations’ “17 Sustainable Development Goals” adopted at the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Our long experience in environmental missions, and especially our strong involvement in the Copernicus programme, will be a great asset for SCARBO,” said Mathilde Royer-Germain, Head of Earth Observation, Navigation and Science in Airbus Space Systems.
The overall measurement concept will be experimentally validated through a dedicated airborne campaign with instrument prototypes in 2020. SCARBO is expected to be ready to work as a complementary system with the second generation of Copernicus satellites within a decade.
The consortium will assess commercial perspectives beyond institutional use of its data products at global, regional and local scales.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s H2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 769032.





